Rather there exists within the spinal cord a gate mechanism that determines the degree to which pain signals are transmitted to the brain. Increasing activity of the transmission cells results in increased perceived pain.
A Schematic Of Melzack And Wall S Gate Control Mechanisms See Text For Download Scientific Diagram
By activating Aβ fibres with tactile non-noxious stimuli inhibitory.
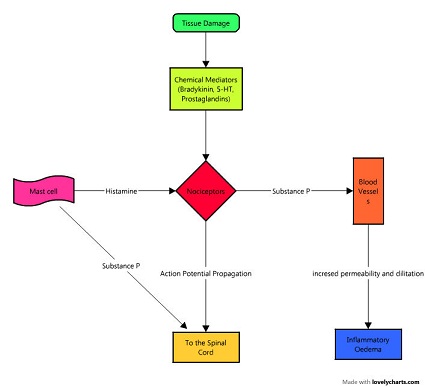
. When the gate is wide open more pain signals get through than when it is. The Gate Control Theory of Pain. Those nerves carry the electrical impulses generated in response to various sensations like touch or any painful stimuli which are.
This theory explains about a pain modulating system. Up to 10 cash back Definition. Gate control theory was described by Melzack and Patric Wall in the year 1965.
According to the Gate Control Theory of Pain 104 the faster conducting non-nociceptive fibers encapsulated large fibers indirectly inhibit the nociceptive fibers stretch reactive free fiber. The inhibitory effect exerted by SG cells onto the primary afferent fiber terminals at the T cells is increased by activity in A-fibers and de-. The gate control theory of pain.
Gate control theory of pain The gate control theory of pain was proposed by Melzack and Wall in 1965 to describe a process of inhibitory pain modulation at the spinal cord level. For example you will probably be aware that there are times when even though you have pain you are only dimly aware of it. The Gate Theory of Pain published by Ronald Melzack and Patrick Wall in Science in 1965 was formulated to provide a mechanism for coding the nociceptive component of cutaneous sensory input.
ArticleMelzack1978TheGC titleThe gate control theory of pain authorRonald Melzack journalBritish medical journal year1978 volume2 6137 pages 586-7 R. There are currently two opposing theories of pain. Although the theory accounts for phenomena that are primarily mental in nature - that is pain itself as well as some of the psychological factors influencing it - its scientific beauty is that it provides a physiological basis for the complex phenomenon of pain.
A New Theory A gate control system modulates sensory input from the skin before it evokes pain perception and response. Rather there exists within the spinal cord a gate mechanism which determines the degree to which pain signals are transmitted to the brain. All sorts of factors influence our experience including our thoughts and feelings.
PubMed Google Scholar Wall PD. The Gate Control Theory. When the gate is wide open more pain signals get through than.
This may happen when you are. Non-noxious stimuli the ones that dont make you feel pain pass through the pain gate and then help close the. For example you will probably be aware that there are times when even though you have pain you are only dimly aware of it.
According to the gate control theory of pain pain signals that originate in an area of injury or disease do not travel directly or automatically to the brain. The gate control theory of pain describes how non-painful sensations can override and reduce painful sensations. I specificity theory which.
Because touch increases large fiber activity it has an inhibitory effect on pain signals. A re-examination and re-statement. It was the first theory to introduce the concept that pain experience is not simply the result of a linear process that begins with the stimulation of pain pathways in the peripheral nervous system and ends with the experience of pain in the central.
The Gate Control Theory of Pain Ver40 November 2020 Page - 3. A painful nociceptive stimulus stimulates primary afferent fibers and travels to the brain via transmission cells. Work TV book then this can distract you from any pain helping to.
The way in which we experience pain is very complex. Wall The nature of pain has been the subject of bitter controversy since the turn of the century 1. The Gate Control Theory of Pain proposes that both large A-fibers and small C-fibers synpase onto cells in the substantia gelatinosa SG and the 1st central transmission T cells.
It does this by. Being involved and taking an interest in life helps to close the gates. It is called the gate control theory of pain and it was initially developed by Ronald Melzack and Patrick Wall.
Ronald Melzack and Patrick D. Conversely decreasing activity of transmission cells reduces. Proposal ofthe gate control theory ofpain is that the flow ofnociceptive nerve impulses from the peripheral nerve system to the central nervous system is modulated in the dorsal horns ofthe spinal column for a recent review see Besson Chaouch 1987This neural mechanism is con sidered to act as a pain gate in which nociceptive trans.
All sorts of factors influence our experience including our thoughts and feelings. The theory dealt explicitly with the apparent conflict in the 1960s between the paucity of sensory neurons that responded selectively to intense stimuli and the well-established finding. Gate control theory is also used to explain why massage and touch can be helpful pain management strategies during childbirth.
For example you will probably be aware that there are times when even though you have pain you are only dimly aware of it. Also if you concentrate intensely on something other than the pain eg. The gate control theory of pain The way in which we experience pain is very complex.
The gate control theory GCT of pain was introduced in 1965 by Ronald Melzack and Patrick Wall. All sorts of factors influence our experience including our thoughts and feelings. The theory is even used to explain the benefits of dance and music for relieving labor pain.
Every part of the human body has its own nerve supply. The pain gate control theory states that gates allow certain stimuli to pass through neural pathways to your brain. It helps to explain why when we bang our head it feels better when we rub it.
The Gate Control Theory of Pain The Gate Control Theory The way in which we experience pain is very complex. The gate control theory of pain mechanisms. According to the gate control theory of pain pain signals that originate in an area of injury or disease do not travel directly or automatically to the brain.

Gate Control Theory Of Pain Youtube

0 Comments